RAID vs MooseFS

Your Network Storage
When it comes to data storage, many organizations turn to RAID as a popular option. RAID technology allows multiple physical hard drives to be combined into a single logical unit, providing improved performance and data redundancy. However, despite its popularity, RAID has its drawbacks and can be dangerous, leading to more risk of data loss and downtime when compared to distributed storage systems like MooseFS.
Points of Failure
One of the primary issues with RAID is the risk of a single point of failure. In most RAID configurations, data is spread across multiple drives, and if one of those drives fails, the data may become inaccessible. Even RAID configurations that offer redundancy through mirroring or parity can be problematic. Mirroring requires twice the number of physical drives and can be costly. Meanwhile, parity-based RAID can suffer from the "write hole" problem, where data corruption can occur due to power outages or unexpected shutdowns.
MooseFS, on the other hand, offers multiple host redundancy. This feature ensures that there is no single point of failure, meaning that even if one or more of the physical drives fails, the data will still be accessible from another node. This redundancy prevents downtime and data loss, providing peace of mind for organizations who store important data or have critical applications that rely on their storage.
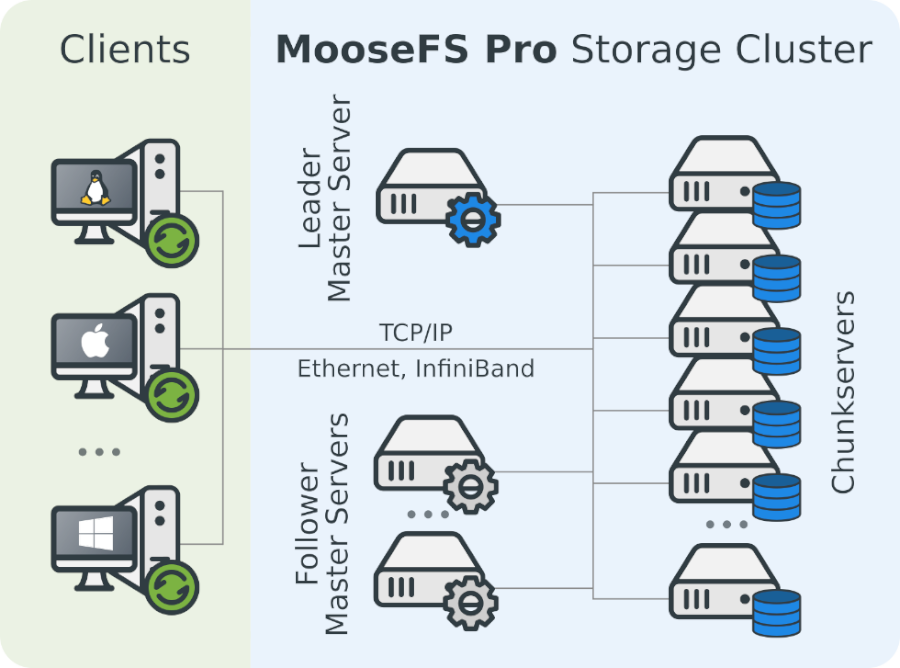
Scalability
Another issue with RAID is scalability. While RAID can provide improved performance and redundancy for small to medium-sized data sets, it can become less effective as data sets grow in size. As the number of drives in a RAID array increases, the risk of a drive failure also increases. This can lead to longer rebuild times and increased downtime.
MooseFS, on the other hand, is designed to be highly scalable and can handle very large data sets with ease. MooseFS uses a distributed file system architecture, allowing data to be spread in chunks across many 'bricks' (disks) on multiple hosts. MooseFS can handle scaling up to petabytes of data, combining the network bandwidth of many hosts for higher speed applications, it offers higher levels of parallelism and scalability then RAID can provide. For organizations that need to store and manage larger amounts of data, MooseFS is an ideal choice.
Data Integrity
Data integrity is also a critical issue in data storage. RAID provides some level of data redundancy, but it does not guarantee data integrity. If data corruption occurs on one drive, the corrupted data may be mirrored or parity-checked onto the other drives, resulting in data loss or corruption across the entire array. RAID uses error correction code algorithms with up to 9 parity sums to ensure data redundancy. However, this approach can be inefficient as it saves less RAW space compared to an ordinary data duplication approach. In contrast, MooseFS ensures data redundancy by using distributed data replication across multiple storage nodes. This means that if one node fails, data can be retrieved from other nodes, eliminating the risk of data loss or downtime.
MooseFS offers the ability to adjust the redundancy of data on a per folder basis. So less important data can be made less redundant to save disk space, while more important data can be set to maximise redundancy and safety. MooseFS also offers efficient atomic snapshotting, ensuring that data integrity is maintained at all times. With atomic snapshotting, MooseFS takes a snapshot of the data at a specific point in time, ensuring that any changes made to the data are not reflected until the snapshot is complete. This approach ensures that even if there is data corruption, the snapshot can be used to restore the data to a known good state.
Another advantageous feature of MooseFS is its virtual, global space for deleted objects, which can be configured for each file and directory. This feature makes it easy to recover accidentally deleted data, a common issue in RAID data storage.
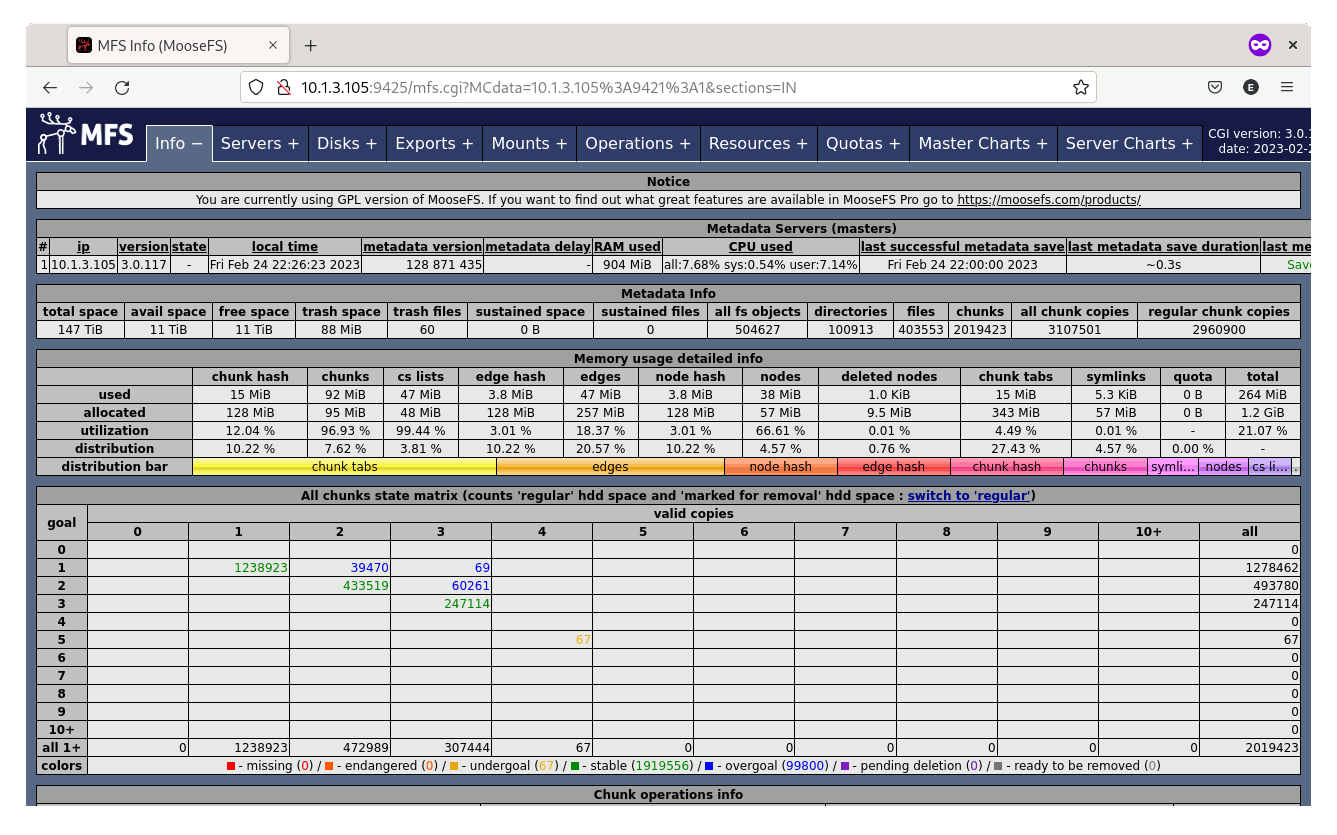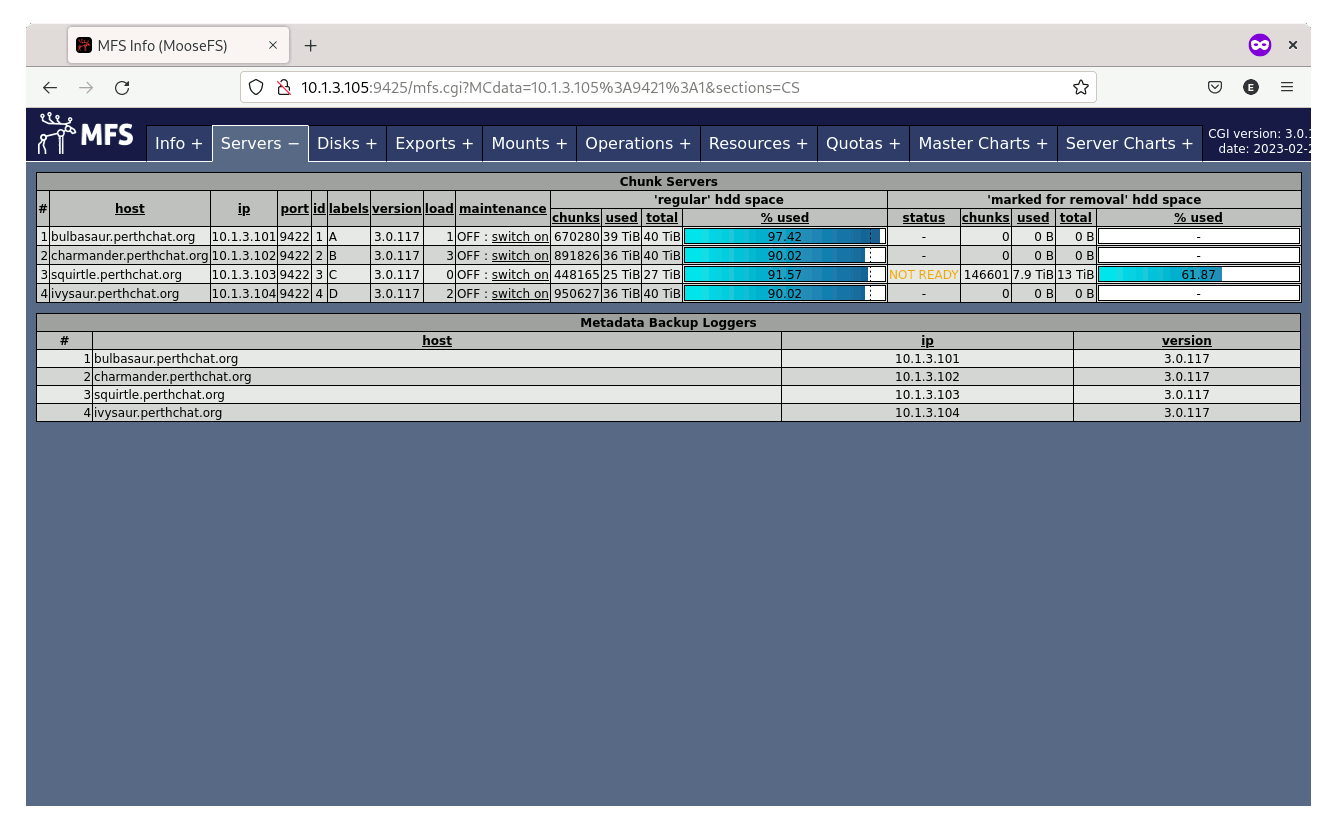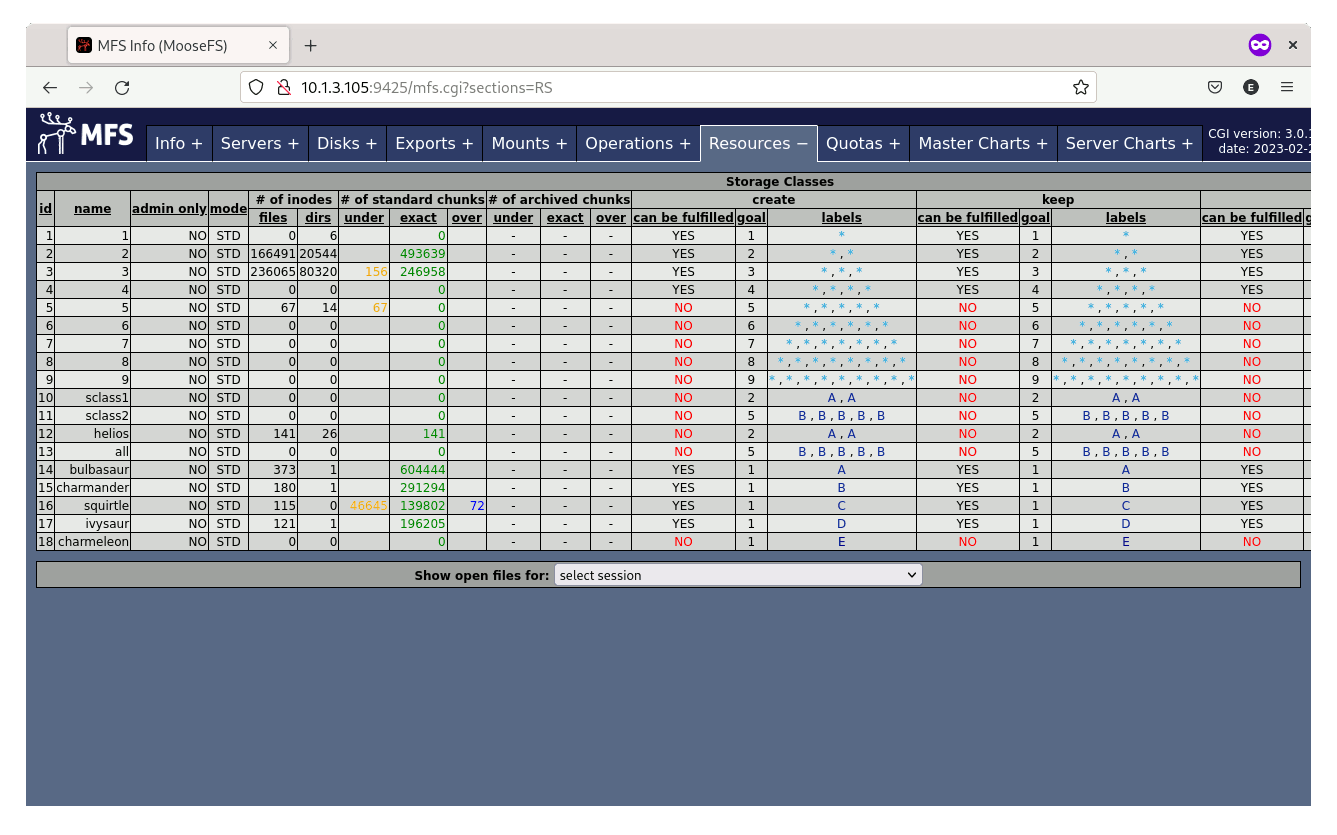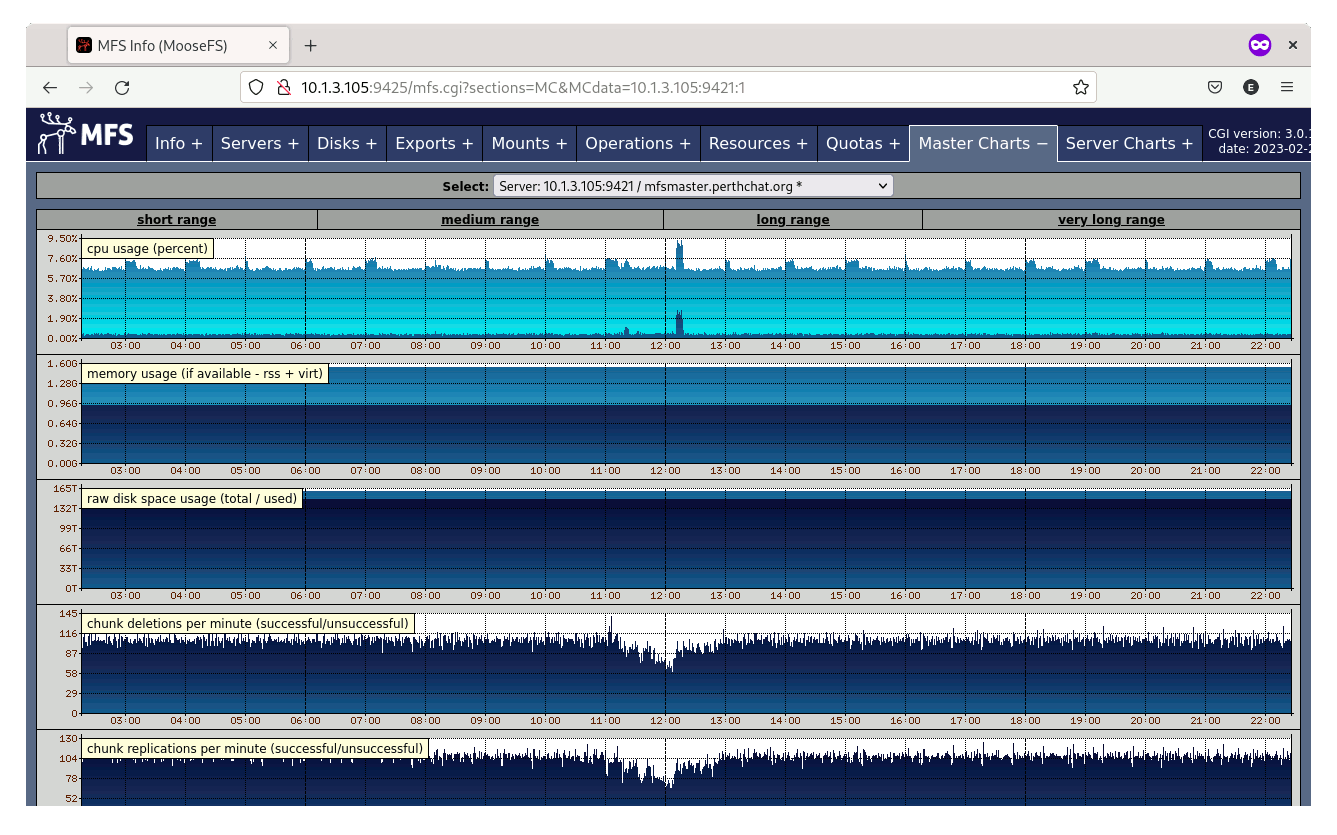
Performance
RAID was initially developed in the 1980s as a means of improving data storage reliability by distributing data across multiple disks. However, as storage technology has advanced, RAID has become less effective and more prone to failure. One of the biggest issues with RAID is that it relies on a single central server or network connection, which can become a bottleneck for I/O operations. This can lead to slower data access times and increased downtime for organizations.
MooseFS Pro offers high availability master nodes to ensure that the file system's central management component is always accessible and reliable. The high availability feature provides redundant master nodes, so that if one master node fails or becomes unreachable, another node can seamlessly take over its functions. This helps to prevent data loss and downtime, ensuring that the system remains available to users even in the event of hardware failures or other issues.
MooseFS Pro's EC (Erasure Coding) feature can save disk space by reducing the amount of redundancy needed to protect data. For example, with a traditional replication-based storage system, you may need to store three copies of your data to ensure data integrity. With EC, you can achieve the same level of data protection with fewer copies and less redundancy. For a 200TB cluster, using replication-based storage, you would need 600TB of raw storage capacity to store three copies of your data. However, with EC, you could achieve the same level of data protection with only 400TB of raw storage capacity, assuming a 2+2 erasure coding scheme. This represents a significant savings in disk space, without sacrificing data integrity.
Hardware Independance
Traditional RAID systems typically require that all disks be uniform in type and size, which can restrict flexibility and drive up costs.
In contrast, MooseFS offers the advantage of supporting both all-flash and hybrid storage setups, allowing for a mix of different manufacturers' disks and servers within a single clustered storage system. This means that the system can accommodate both older and newer technology, as well as both consumer-grade and enterprise-grade hardware. Furthermore, MooseFS allows hosts with different operating systems to be combined, enabling seamless integration with various environments. With MooseFS, users can easily and incrementally scale up their storage capacity as their needs and budget change, or alternatively downsize and repurpose hardware as needed, providing a highly flexible and cost-effective storage solution.
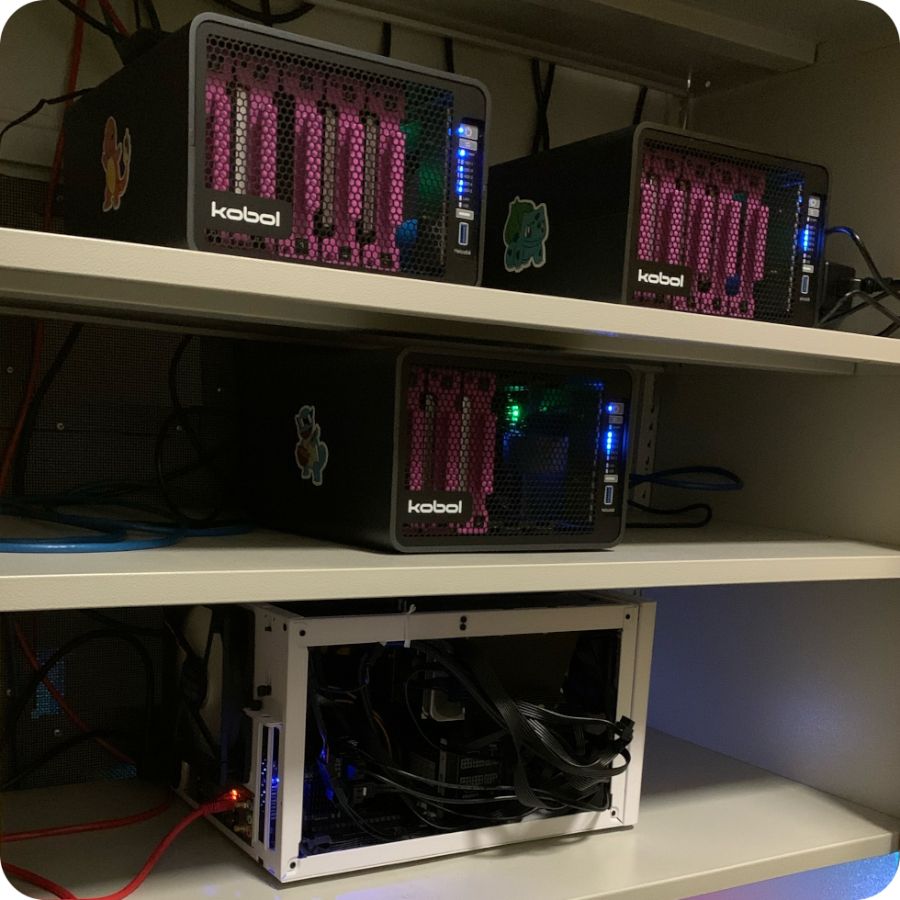
Here we see my own MooseFS cluster that combines a consumer grade amd64 computer with 3 low power arm64 Helios64 devices:

Summary
In conclusion, while RAID has been a popular choice for many years, it is not without its drawbacks. RAID can be dangerous and can cause more downtime when compared to MooseFS Community Edition or Pro. MooseFS offers multiple host redundancy ensuring there's no single point of failure, efficient atomic snapshotting, high reliability, parallelism, and scalability. These features make MooseFS an excellent choice for organizations looking to store and manage large amounts of data while minimizing the risk of downtime and data loss. Overall, these features make MooseFS a superior option for organizations looking for a reliable and efficient storage system.
Are you interested in running MooseFS? You might also enjoy my more recent article about configuring basic failover with MooseFS Community Edition.